IoT, Edge Computing, and Digitalization in Healthcare
COVID-19 accelerated the digitization of healthcare, contributing to growing IoT adoption and exploding health data volumes. This digital transformation helps to improve efficiency and reduce costs, while opening new avenues for enhanced patient experience and well-being. Simultaneously, growing data privacy concerns, increasing costs, and heavier regulatory requirements are challenging the use of cloud computing to manage this data. A megashift to Edge Computing is addressing these challenges enabling a faster, safer and more reliable digital healthcare infrastructure.
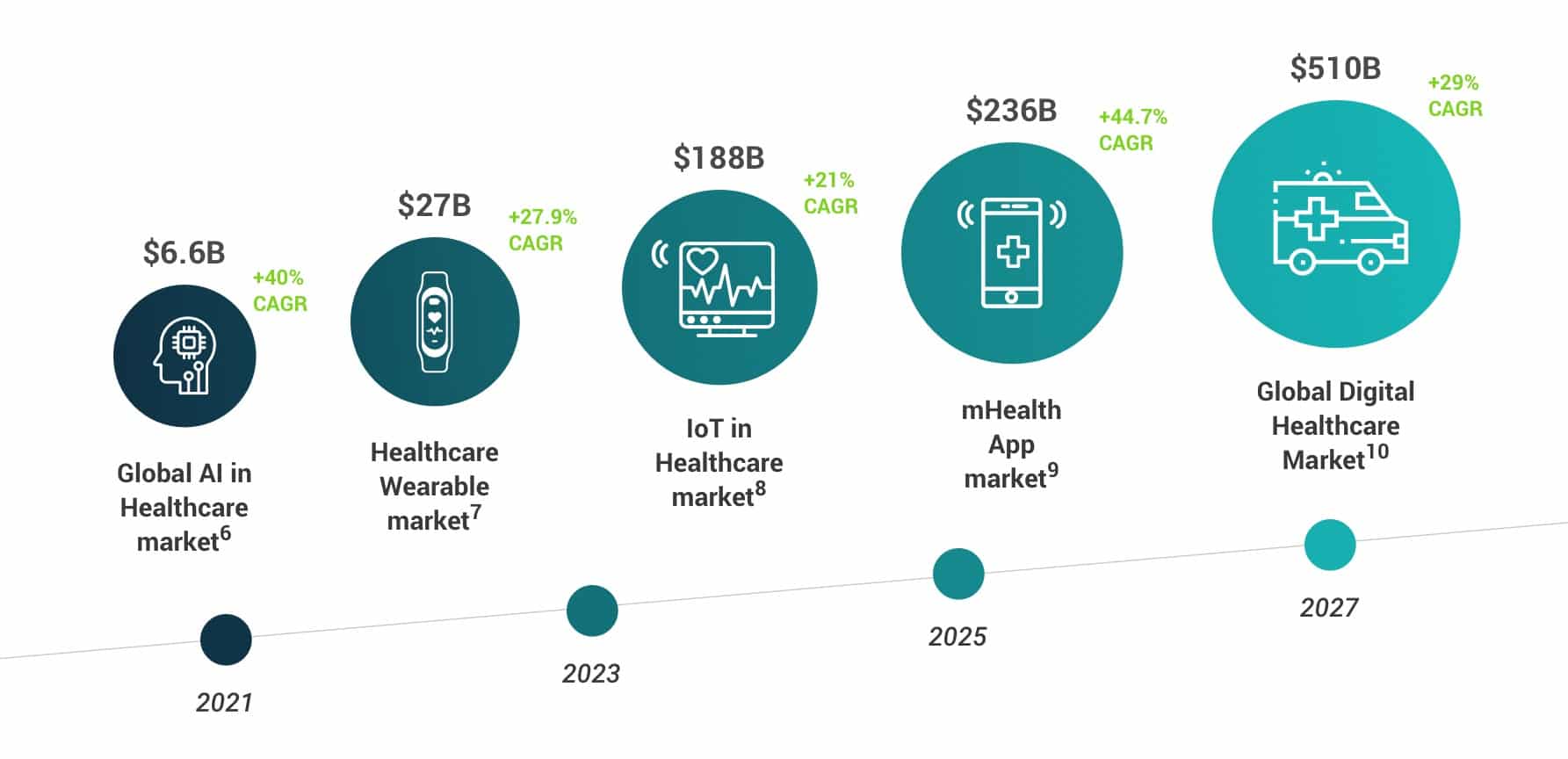
The digital healthcare market 2020 and beyond, a high speed revolution
Prior to COVID, growth in digital health adoption stalled. [1] However, digitalization in the healthcare industry has sky-rocketed since the start of the pandemic. Reflecting this market turnaround, the third quarter of 2020 was a record year for investments in healthcare companies. [2] A trend that will continue in the next years, as analysts predict rapid growth across digital healthcare market sectors:
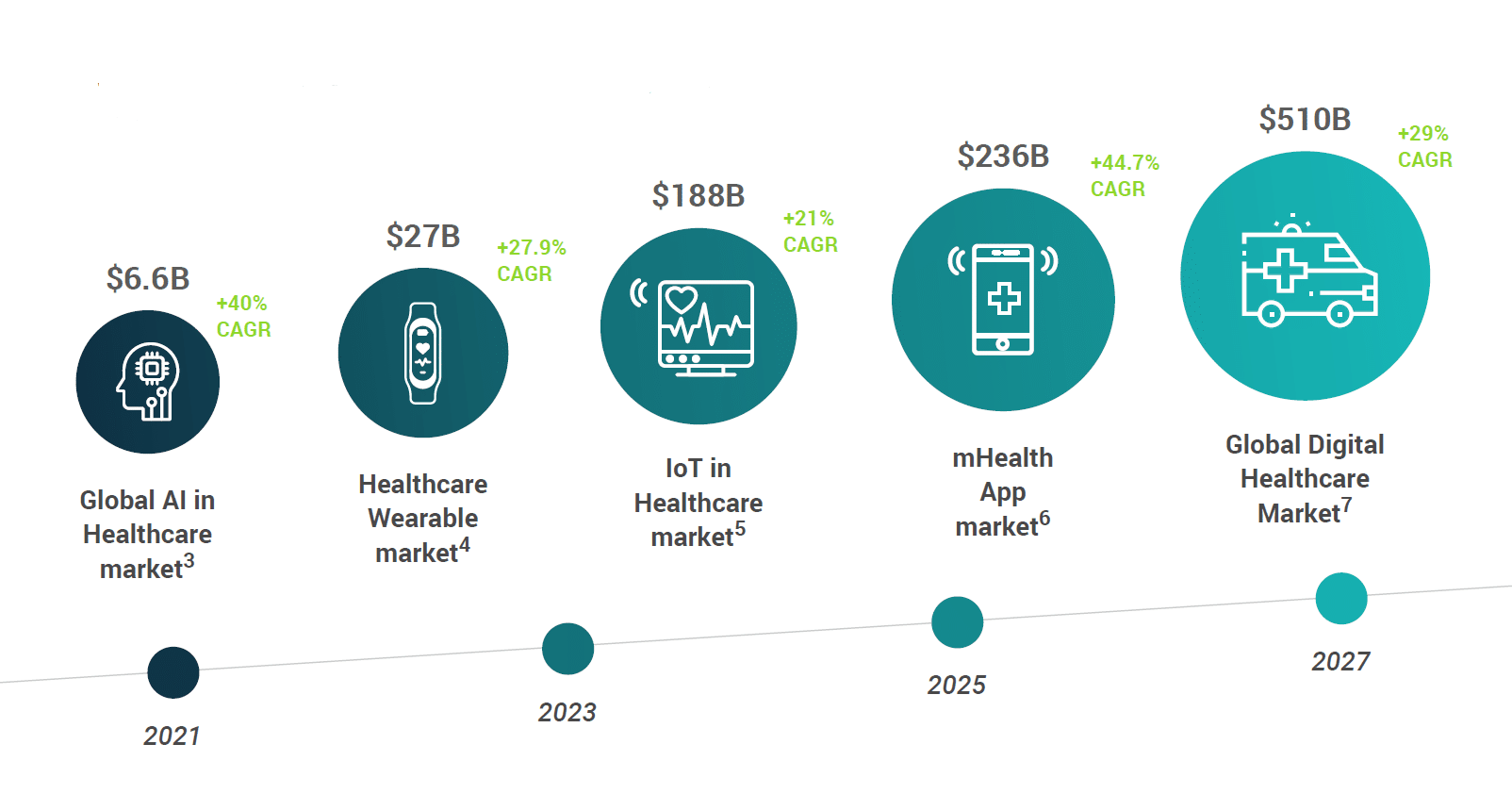
Drivers of growth and change in digital healthcare
Digital Healthcare Growth Driver 1: COVID
The COVID pandemic accelerated the digitization of healthcare, pushing doctors, patients – and their data – to the virtual world. [8] The year 2020 marks the tipping point for digital healthcare offerings. With healthcare providers and patients forced to use digital means, adoption barriers have been removed for good. Indeed, a recent study from Forrester indicates that 36% of adults found that the care they received virtually was just as effective as what they would have received in person, and over 30% of adults will seek virtual care again in the future. [9]
Over 30% of adults will seek
virtual care again in the future
Digital Healthcare Growth Driver 2: Growing Medical IoT Device Adoption
There will be a projected 55 billion IoT devices by 2025. [10] Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) are hardware devices designed to process, collect, and/or transmit health related data via a network. IoMT devices are projected to make up 30% of the entire IoT device market by 2025. [11] According to Gartner, 79% of healthcare providers are already using IoT in their processes, [12] i.e. remote health monitoring via wearables, ingestible sensors, [13] disinfection robots, [14] or closed-loop insulin delivery systems.15 IoMT devices increase safety and efficiency in healthcare, and future technical applications, like smart ambulances or augmented reality glasses that assist during surgery, are limitless.
IoMT devices are projected to make up
30% of the IoT device market by 2025

Digital Healthcare Growth Driver 3: The Explosion of Health Data
Growing IoMT adoption is subsequently driving a rapid increase in the amount of collected health data. According to an IDC study, healthcare data is growing exponentially projected 36% CAGR through 2025; health data is expected to eclipse data volumes from sectors like manufacturing, financial services, and media. [16] The increase in healthcare data opens up new opportunities to apply technology to improve healthcare like e.g. big data analysis, AI and ML. In fact, the healthcare analytics market is expected to reach $84.2 billion by 2027 with a 26% CAGR. [17]

Healthcare data will experience a
36% CAGR through 2025
Digital Healthcare Growth Driver 4: Technological innovations: Edge Computing, AI, and VR
Big health data sets are being used to revolutionize healthcare, bringing new insights into fields like oncology,18 and improving patient experience, care, and diagnosis: “Taken together, big data will facilitate healthcare by introducing prediction of epidemics (in relation to population health), providing early warnings of disease conditions, and helping in the discovery of novel biomarkers and intelligent therapeutic intervention strategies for an improved quality of life.” [19] In a November 2020 survey from Intel, 84% of healthcare providers shared that Artificial Intelligence deployments had occurred or were planned in their clinical workflow, an increase from 37% in 2018. This is unsurprising, as AI technologies are predicted to save the healthcare industry up to $150 billion per year, by answering “20 percent of
unmet clinical demand.” [20]
Augmented and Virtual Reality are also finding a place in healthcare settings. VR tools have been shown to reduce pain, [21] and are being used in therapy as a means to help patients overcome painful and traumatic experiences. Experts expect a realm of future AR applications in the operating room, assisting doctors during surgical procedures.
Current or planned AI deployments are at
84% in 2020, up from 37% in 2018
Digital Healthcare Growth Driver 5: Underlying Social Megatrends
The global population is growing; global life expectancy is rising. Accordingly, by 2030 the world needs more energy, more food, more water. Explosive population growth in some areas versus declines in others contributes to shifts in economic power, resource allocation, societal habits and norms. Many Western populations are aging rapidly. E.g. in America, the number of people 65+ is expected to nearly double to 72.1 million by 2034. Because the population is shrinking at the same time, elder care is a growing challenge and researchers are looking to robots to solve it. [22]
Health megatrends focus not only on the prevention of disease, but also on the perception of wellness, and new forms of living and working. Over the coming decade more resources will be spent on health and longevity, leading to artificially and technologically enhanced human capabilities. More lifestyle-related disorders and diseases are expected to emerge in the future. [22]
A focus on health and longevity will
lead to artificial & tech enhanced
human capabilities
The Challenges of Healthtech
Along with more data, more devices and more opportunity also comes more
responsibility and more costs for healthcare providers.
Data Volume and Availability With the growing number of digital healthcare
and medical devices, a dazzling volume of health data is created and collected across many different channels. It will be vital for the healthcare industry to reliably synchronize and combine data across devices and channels. [23] Due to the sheer volume, reliable collection and analysis of this data is a major challenge. After it’s been processed, data needs to be available on demand, i.e. in emergency situations that require reliable, fast, available data.
Reliability, Privacy, and Data Security are extremely important in health
technology; 70% of healthcare consumers are concerned about data privacy. [24] Data use is often governed by increasingly strict national regulation, i.e. HIPAA (USA) and / or GDPR (Europe). [25] With the number of cyber-attacks in the healthcare industry on the rise, [26] healthcare professionals must be even more diligent about the storage and processing of data. In addition, healthtech must be extremely well vetted; failures can cost lives – typical “banana products”, which ripen with the customers, are a no-go.

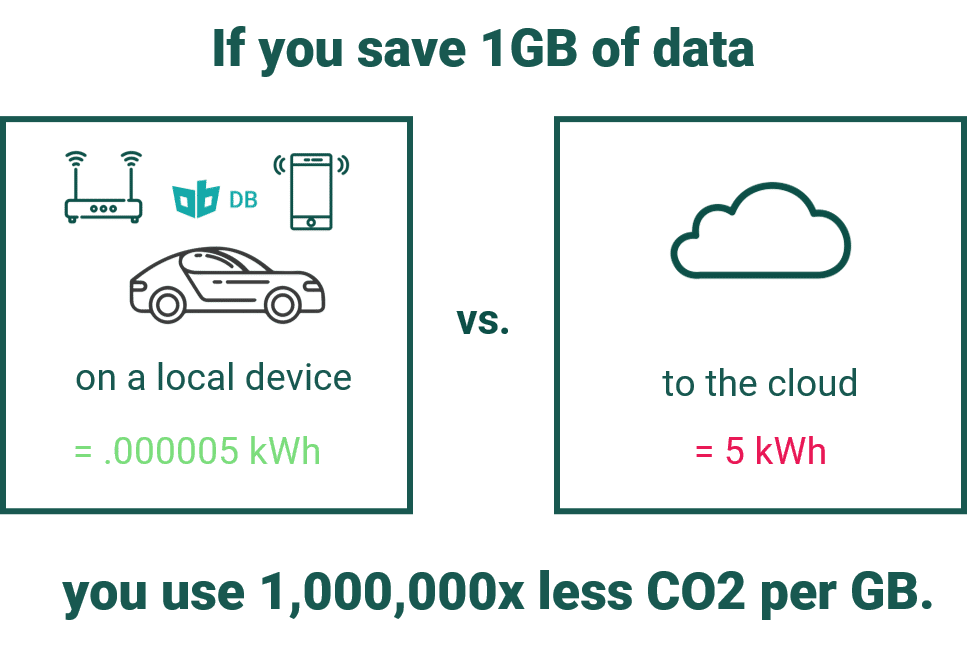
IT Costs Medical devices contribute a large portion to healthcare budgets.
However as data volumes grow, data costs will also become a relevant cost
point. Sending all health data to the cloud to be stored and processed is not
only slow and insecure, it is also extremely costly. To curb mobile network and
cloud costs, much health data can be stored and processed at the edge, on
local devices, with only necessary data being synced to a cloud or central
server. By building resilient data architecture now, healthcare providers (e.g.
hospitals, clinics, research centers) can avoid future costs and headache.
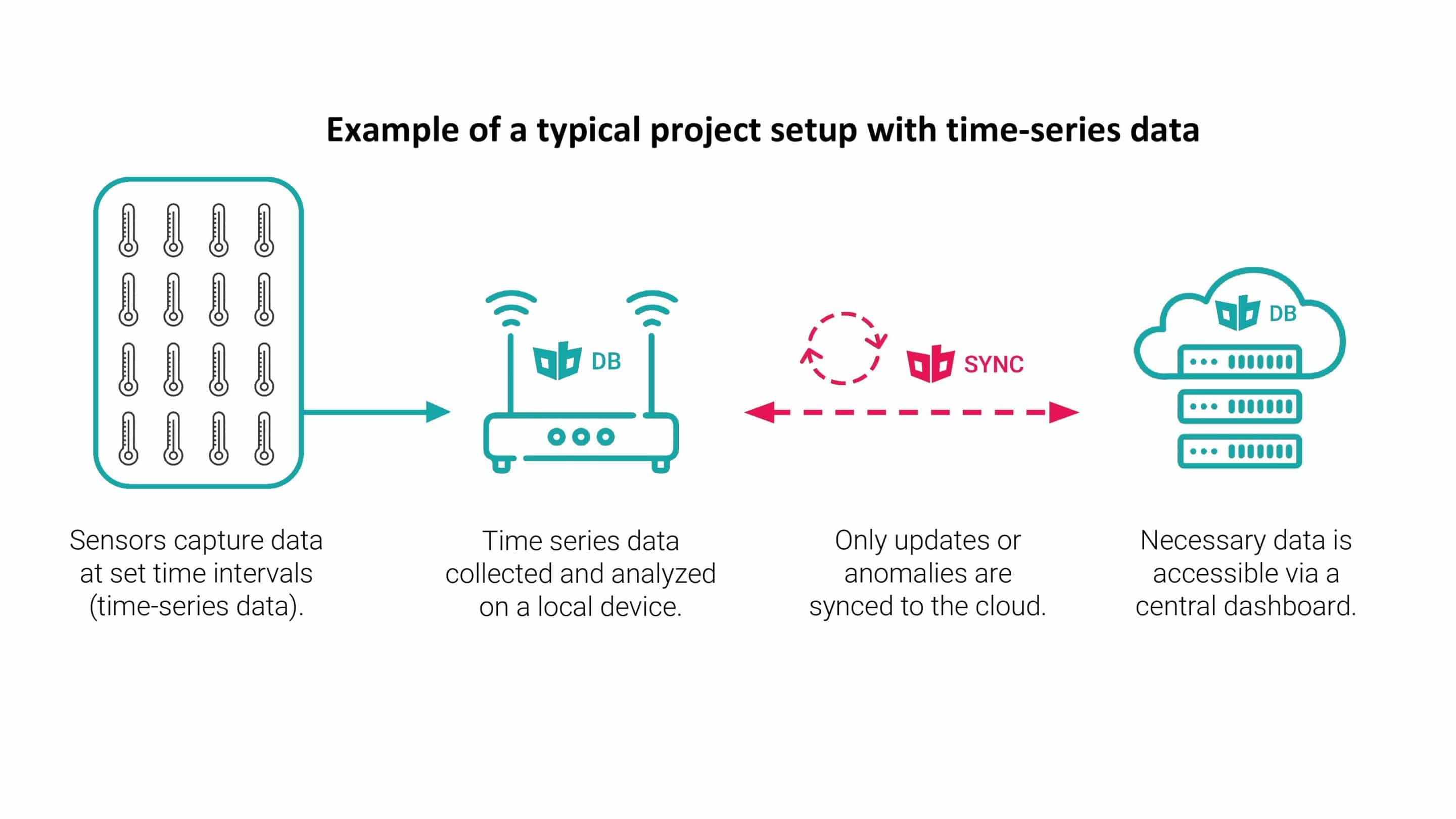
Edge Computing is Integral to Data-driven Healthcare Ecosystems
With big data volumes, industries like healthcare need to seek out resilient information architectures to accommodate growing numbers of data and devices. To build resilient and secure digital infrastructure, healthcare providers will need to utilize both cloud computing and edge computing models, exploiting the strengths of both systems.
Cloud & Edge: What’s the Difference?
Cloud Computing information is sent to a centralized data center, to be stored, processed and sent back to the edge. This causes latency and higher risk of data breaches. Centralized data is useful for large scale data analysis and the distribution of data between i.e. hospitals and doctors’ offices.
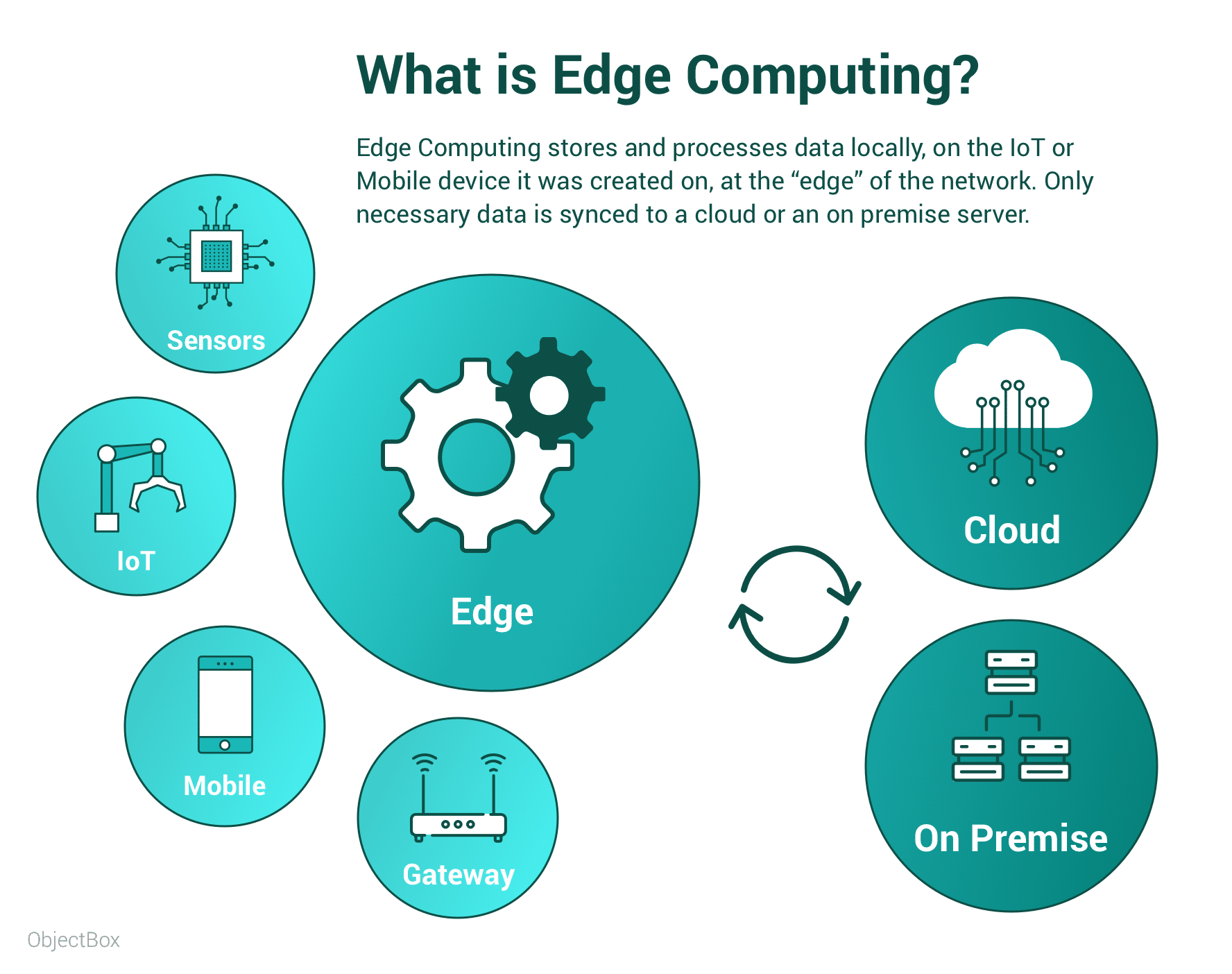
Edge Computing Data is stored and processed on or near the device it was created on. Edge Computing works without an internet connection, and thus is reliable and robust in any scenario. It is ideal for time sensitive data (real time), and improved data privacy and security.
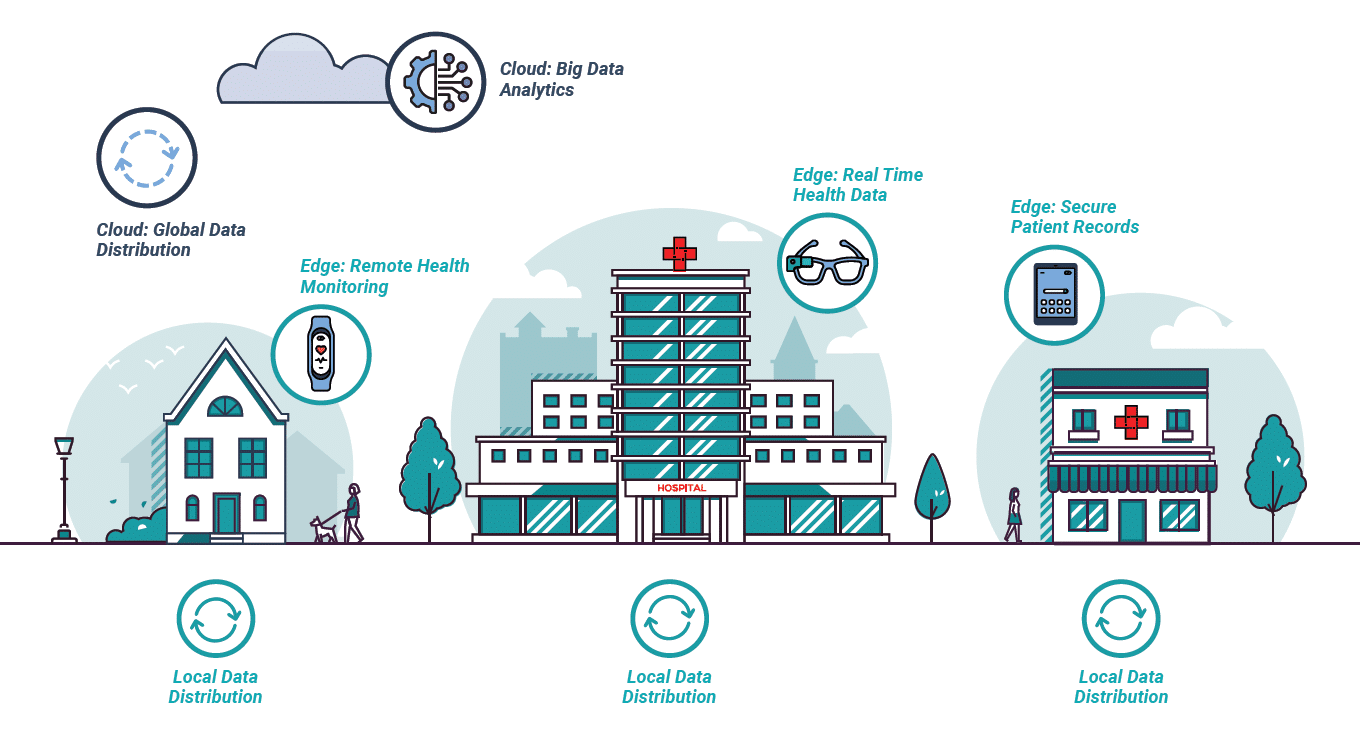
Edge Computing contributes to resilient and secure healthcare data systems
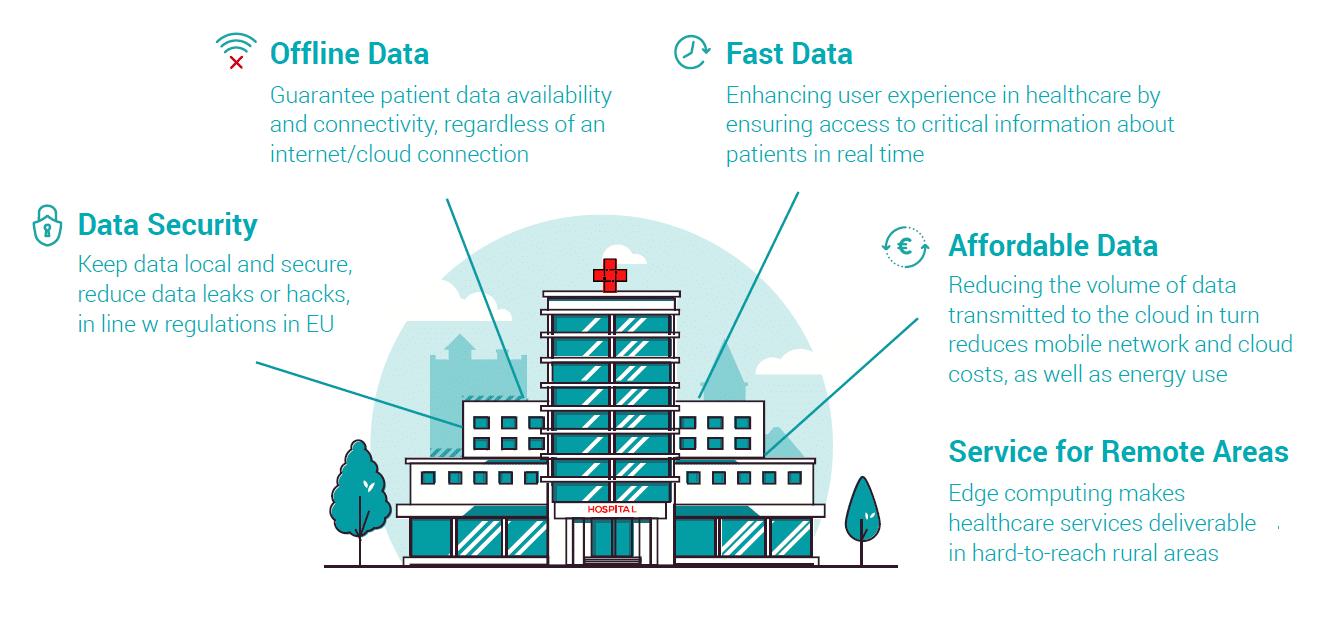
Transforming Healthcare with Edge Computing
Use Case: Secure and Up to Date Digital Record Keeping in Doctors Offices
For private doctors offices, embracing digitalization comes with different hurdles than larger healthcare providers. Often, offices do not keep a dedicated IT professional on staff, and must find digital solutions that serve their needs, while allowing them to comply with ever-increasing data regulations. As an industry used to legislative challenges, GPs know that sensitive patient data must be handled with care.
Solution providers serving private doctors offices are using edge databases to help keep patient data secure. An edge database allows private GPs to collect and store digital data locally. In newer practice setups, doctors use tablets, like iPads, throughout their practice to collect and track patient data, take notes and improve flexibility. This patient data should not be sent or stored in a central cloud server as this increases the risk of data breaches and opens up regulatory challenges. In a cloud-centered set up, the doctor also always needs to rely on a constant internet connection being available, making this also a matter of data availability

Accordingly, the patient data is stored locally, on the iPads, accessible only by the doctor treating the patient. Some of the data is synchronized to a local, in-office computer at the front desk for billing and administration. Other data is only synchronized for backup purposes and encrypted. Such a setup also allows synchronizing data between iPads, enabling doctors to share data in an instant.
Use Case: Connected Ambulances – Real Time Edge Data from Home to Hospital
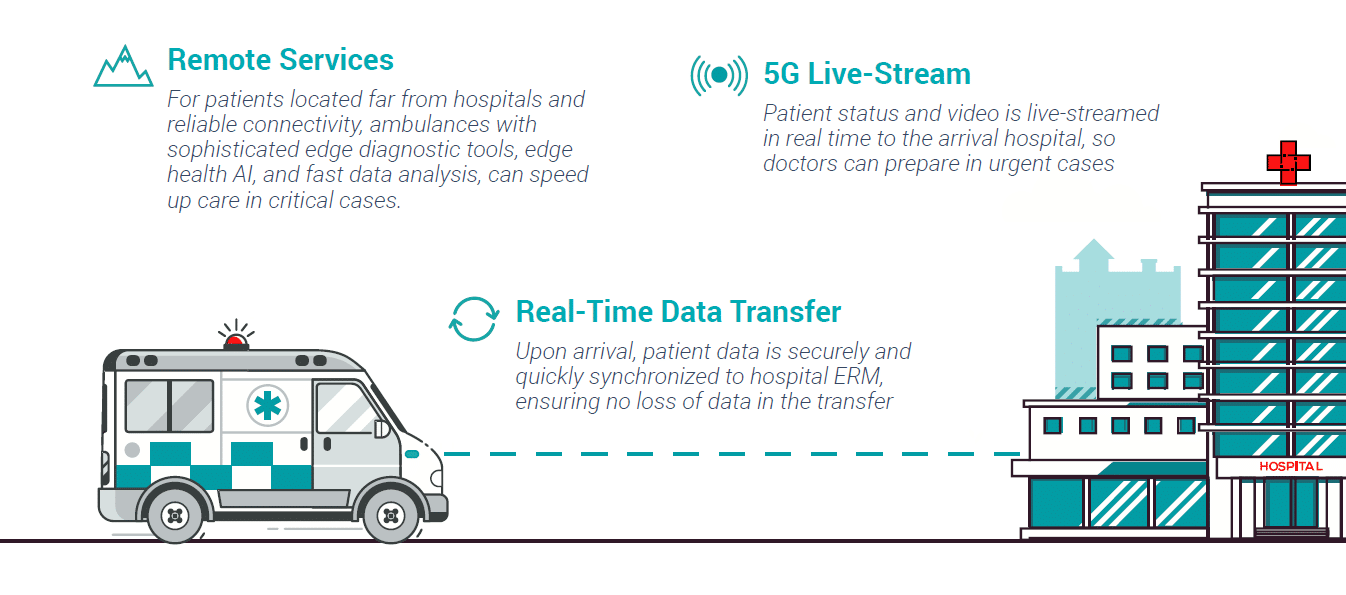
Between an incidence location and the hospital, a lot can happen. What if everything that happened in the ambulance was reliably and securely tracked and shared with the hospital, seamlessly? Already there are trials underway using 5G technology to stream real time data to hospitals, [27] and allowing ambulance medics to access patient data while in transit. [28] Looking to the future, Edge Computing will enable digital healthcare applications to function in realtime and reliably anywhere and anytime, e.g. a moving ambulance, in the tunnel, or a remote area, enabling ambulance teams and doctors to give the best treatment instantly / on-site, while using available bandwidth and networks when available to seamlessly synchronize the relevant information to the relevant healthcare units, e.g. the next hospital. This will decrease friction, enhance operational processes, and improve time to treatment.
Digital Healthcare: Key Take-Aways
Digital healthcare is a fast-growing industry; more data and devices alongside new tech are empowering rapid advances. Finding ways to utilize growing healthcare data, while ensuring data privacy, security and availability are key challenges ahead for healthcare providers. The healthcare industry must find the right mix of technologies to manage this data, utilizing cloud for global data exchange and big data analytics, while embracing Edge Computing for it’s speed, security, and resilience.

Underutilized data plays a major role in health-tech innovation, [29] data is the lifeline of future healthcare offerings; however, there is still much work to be done to improve the collection, management and analysis of this data.

It’s all about data availability. Either in emergency situations, or simply to provide a smooth patient experience, data needs to be fast, reliable, and available: when you need it where you need it.

Edge computing alongside other developing technologies like 5G, Augmented and Virtual Reality, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning will empower a new and powerful digital healthcare ecosystem.
ObjectBox provides edge data software, to empower scalable and resilient digital innovation
on the edge in healthcare, automotive, and manufacturing. ObjectBox’ edge database and
data synchronization solution is 10x faster than any alternative, and empowers applications
that respond in real-time (low-latency), work offline without a connection to the cloud,
reduce energy needs, keep data secure, and lower mobile network and cloud costs.
Sources
1. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/health/leaders-make-recent-digital-health-gains-last
2. https://www.cbinsights.com/research-state-of-healthcare-q3-2020
3. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insight-artificial-intelligence-healthcare%C2%A0
4. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/wearable-medical-devices-market
5. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/iot-healthcare.asp
6. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-mhealth-app-market
7. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2020/05/23/2037920/0/en/Global-Digital-Health-Market-was-Valued-at-USD-111-4-billion-in-2019-and-is-Expected-to-Reach-USD-510-4-billion-by-2025-Observing-a-CAGRof-29-0-during-2020-2025-VynZ-Research.html
8. https://www.sciencemag.org/features/2020/11/telemedicine-takes-center-stage-era-covid-19
9. https://go.forrester.com/blogs/will-virtual-care-stand-the-test-of-time-if-youre-asking-the-question-its-time-tocatch-up/
10. https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/foresight/topic/accelerating-technological-change-hyperconnectivity/hyperconnectivity-iot-digitalisation_en
11. https://mobidev.biz/blog/technology-trends-healthcare-digital-transformation
12. https://www.computerworld.com/article/3529427/how-iot-is-becoming-the-pulse-of-healthcare.html
https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3970072
13. https://science.sciencemag.org/content/360/6391/915
14. http://emag.medicalexpo.com/disinfection-robots-against-covid-19/
15. https://www.theverge.com/2019/12/13/21020811/fda-closed-loop-insulin-system-software-diabetes-tandemcontrol-iq
16. https://www.seagate.com/files/www-content/our-story/trends/files/idc-seagate-dataage-whitepaper.pdf
17. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/healthcare-analytics-market-worth-84-2-billion-by-2027–growingat-a-cagr-of-26-from-2020–pre-and-post-covid-19-market-opportunity-analysis-and-industry-forecasts-bymeticulous-research-301117822.html
18. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41437-020-0303-2
19. June 2019, https://journalofbigdata.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40537-019-0217-0
20. https://www2.stardust-testing.com/en/the-digital-transformation-trends-and-challenges-in-healthcare
21. https://www.geekwire.com/2018/snowworld-melts-away-pain-burn-patients-using-virtual-reality-snowballs/
22. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/government-public-services/assets/five-megatrends-implications.pdf
23. https://www2.stardust-testing.com/en/the-digital-transformation-trends-and-challenges-in-healthcare
24. https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-133/Accenture-Digital-Health-Tech-Vision-2020.pdf#zoom=40
25. https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=99b83b76-3f2f-4b23-a5c3-30ad576af369
26. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/cyberattack-threat-to-health-care-providers-on-the-rise
https://www.healthcareitnews.com/news/fbi-hhs-warn-increased-and-imminent-cyber-threat-hospitals
https://blogs.microsoft.com/on-the-issues/2020/11/13/health-care-cyberattacks-covid-19-paris-peace-forum/
27. https://www.vodafone.co.uk/business/5g-for-business/5g-customer-stories/connected-ambulance
28. https://www.digitalhealth.net/2019/04/london-ambulance-access-patient-data/
29. https://news.crunchbase.com/news/for-health-tech-startups-data-is-their-lifeline-now-more-than-ever/